Physical Geology
The comprehensive contents from this book, combined with Odigia’s Teaching and Learning Tools have everything you need to engage, collaborate, track and assess your students.
Helping Teachers Do What They Do Best: Teach

Customize
Use our courses as is or easily customize them to fit your teaching style and the needs of your students. You can add your favorite resources, hide and show our existing content and pre-built assessments, or make them your own. Everything your students need, in one place!

Engage and Collaborate
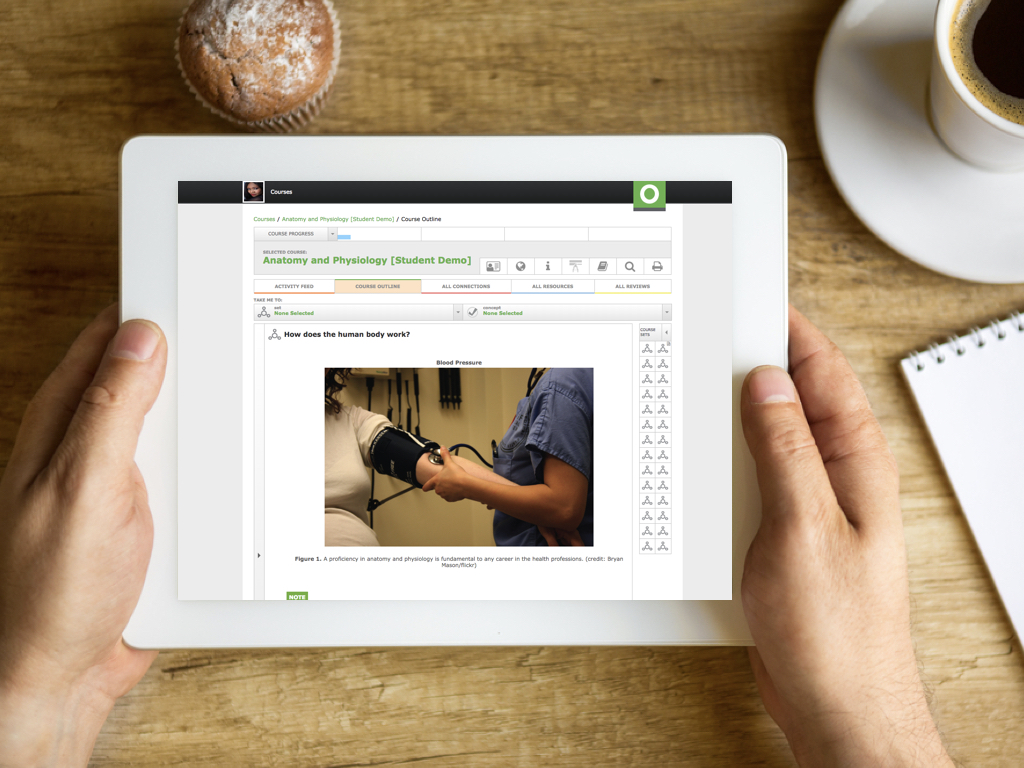
Odigia combines learning materials, discussions, and tools to create a familiar social experience for students allowing you to easily connect and redirect students attention.

Track
See how much time students are spending on different areas of the course, which areas are creating the most amount of engagement and identify topics the students are struggling with. Flag and provide feedback on assignments to proactively meet individual students' needs.

Assess
Game theory allows students to monitor their progress visually and motivates them to stay on track. Students can see exactly what activities they need to complete, which ones have been flagged and compare their progress against the overall class.
Physical Geology Course Outline
Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered: Concepts Covered:Introduction To Geology
Minerals
Intrusive Igneous Rocks
Volcanism
Weathering and Soil
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks
Metamorphism and Metamorphic Rocks
Measuring Geological Time
The Earth's Interior
Plate Tectonics
Earthquakes
Geological Structures
Streams and Floods
Ground Water
Mass Wasting
Glaciation
Shorelines
The Geology of the Oceans
Climate Change
Geological Resources
The Geological History of Western Canada
The Origin of Earth and the Solar System
About the book
Physical Geology

This book was born out of a 2014 meeting of earth science educators representing most of the universities and colleges in British Columbia, and nurtured by a widely shared frustration that many students are not thriving in our courses because textbooks have become too expensive for them to buy.
About the authors:
Senior Contributing Author, Steven Earle
Steven Earle was born in the Okanagan Valley of British Columbia. He earned a BSc in geology from the University of British Columbia in 1975 and a PhD in geochemistry from Imperial College (London University) in 1982. He worked as a geologist and geochemist in the mineral exploration industry in western Canada from 1978 to 2000. For 20 years he developed and taught a wide range of earth science courses at Vancouver Island University. He currently designs and teaches distance courses for Thompson Rivers University (Open Learning), and also helps to grow food and drive the Community Bus on Gabriola Island. He maintains that the best way to see rocks is from a kayak.
